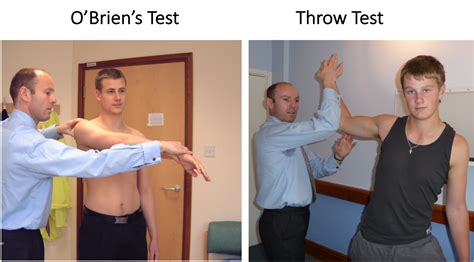
slap tear shoulder tests|special test for slap tear : manufacturing The purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2] Technique. With the patient in sitting or standing, the upper extremity to be tested is placed in 90° of shoulder . Extremely easy without any challenges and trouble. Self-sufficient no need to download .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB1 de fev. de 2024 · Check with your doctor as soon as possible if any of the following side effects occur: For bulk-forming-containing. Difficulty in breathing intestinal blockage skin .
The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) . See moreYour shoulder is a large and complex joint. The O’Brien test focuses on your AC joint and labrum. Your AC joint is one of four shoulder joints, where two bones . See more
Healthcare providers who may perform the O’Brien test include: 1. Athletic trainers. 2. Orthopedists(bone and joint specialists). 3. Physical therapists. 4. . See moreThe purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2] Technique. With the patient in sitting or standing, the upper extremity to be tested is placed in 90° of shoulder .The physical examination: A combination of two sensitive tests and one specific test is useful to diagnose a SLAP lesion. Sensitive tests include: Compression rotation test; O’Briens test; Apprehension Test; Specific tests include: Speed’s test; Yergason’s test; Biceps load test II A SLAP lesion (Superior Labrum from Anterior to Posterior tear) generally occurs as result of overuse injury to the shoulder in overhead athletes or traumatic falls in older patients and can result in deep shoulder pain and .
Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and .
An MRI scan can show soft tissues, like the labrum, better than an X-ray. Sometimes, a special type of MRI, called an MRI arthrogram, is needed to see the SLAP tear. This test is performed by injecting dye into your shoulder before .
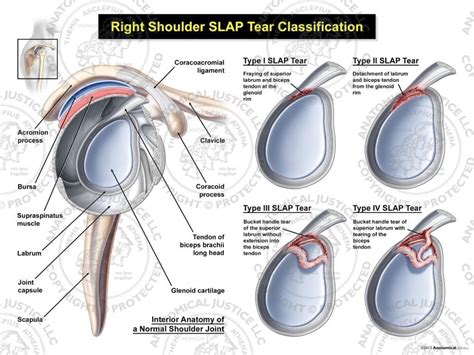
They recommend that a combination of at least 3 positive SLAP lesion tests may be clinically useful in diagnosing a shoulder SLAP lesion with greater diagnostic accuracy. Combo of Tests. The combination of the Biceps Load I/II and . The shoulder labrum is a cup-shaped rim of rubber-like fibrous cartilage that lines the socket to help secure the humerus and reinforce the joint. Also known as the glenoid labrum, it provides support and stability to the . Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tear refers to a specific injury of the superior portion of the glenoid labrum that extends from anterior to posterior in a curved .
The best tests available to make the diagnosis of a labral tear are magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans or a test called a CT-arthrogram (the latter is a CAT scan preceded by an arthrogram where dye is injected into the .Biceps load test II: a clinical test for SLAP lesions of the shoulder. Arthroscopy 2001 February; 17(2):160-164. ↑ 2.0 2.1 Somerville L, Willits K, Johnson A, Litchfield R, LeBel ME, Moro J, et al. Clinical Assessment of Physical .
A SLAP tear of the shoulder is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder joint. SLAP tears typically cause pain when performing overhead activities. . can be indicative of a SLAP tear. Crank test: This test is .
These tears are common in overhead throwing athletes and laborers involved in overhead activities. The pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and nonsurgical management of SLAP tears are reviewed here. The general approach to patients with shoulder pain, the shoulder examination, and rotator cuff injuries are discussed separately. Superior labral anterior to posterior (SLAP) lesions constitute a recognized clinical subset of complex shoulder pain pathologies. SLAP lesions demonstrate a predilection for young laborers, overhead athletes, and middle-aged manual laborers.[1] In 1985, Andrews first described superior labral pathologies, and Snyder later coined the term “SLAP lesion” because of the .
The common symptoms of a SLAP tear are similar to many other shoulder problems. They include: A sensation of locking, popping, catching, or grinding . like the labrum, better than an X-ray. Sometimes, a special type of MRI, called an MRI arthrogram, is needed to see the SLAP tear. This test is performed by injecting dye into your shoulder . The acronym “SLAP” stands for Superior Labrum Anterior-Posterior. It describes a tear or detachment of the shoulder’s superior glenoid labrum, generally originating at the anchor site for the biceps tendon’s long head and extending into .
What do they Recommend to diagnose a slap tear? They recommend that a combination of at least 3 positive SLAP lesion tests may be clinically useful in diagnosing a shoulder SLAP lesion with greater diagnostic accuracy. Combo of Tests. The combination of the Biceps Load I/II and O’Brien’s showed the highest sensitivity and specificity.The exam of the shoulder has to be completed by some specialized tests and provocative maneuvers that are specific for different shoulder lesions and pathologies. These tests will help us confirm or exclude the presence of a specific shoulder condition, that we may only suspect after the inspection and the assessment of the full range of motion.
special test for slap tear
This test also called labral crank test or compression rotation test is used to identify glenoid labral tears and assess an unstable superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) lesions. . load is applied along the axis of the humerus with one hand while the other hand performs humeral rotation while the shoulder is being elevated in the . Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tears are a subset of labral pathology in acute and chronic/degenerative settings. First described in the 1980s, extensive study has followed to elucidate appropriate evaluation and management.[1] Patient-specific considerations and appropriate utilization of both non-surgical and surgical interventions are of the utmost .Labral Tear: The test is particularly useful for identifying superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) lesions. Instability: Helps in diagnosing shoulder instability, especially in athletes. Evidence [edit | edit source] The sensitivity and specificity of .SLAP Lesion Cluster 1 | Shoulder Assessment. According to a study done by Schlechter et al. (2009), a combination of the Active Compression Test and the Passive Distraction test yields a positive likelihood ratio of 7.0 for 2 positive tests and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.33 for two negative tests. This test cluster therefore has moderate clinical value to confirm or rule out .
SLAPprehension Test. Jo Gibson. This test was described by Berg and Ciullo in 1998 and was developed after 2 patients described cervical spine and shoulder pain and a click associated with turning a steering wheel Le. horizontal flexion and internal rotation after RTA. Arthroscopy revealed the presence of a type II SLAP lesion in both patients.. Test. The patient is examined . There are many different kinds of shoulder labrum tears. A labrum SLAP tear covers a specific area. The upper, or superior, part of your labrum attaches to your biceps tendon. In a labrum SLAP .Posterior labrum tear: This tear occurs at the back of the shoulder joint. SLAP tear: A superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tear occurs at the top of the glenoid (shoulder socket) and extends from the front to the back, where the . 7. Examination to detect a SLAP tearDr. Mark Hutchinson's Knee, Shoulder and Hip/Groin Exam is a combined project of the University of British Columbia (UBC).
SLAP tear surgery is recommended when: You still have SLAP tear symptoms despite non-surgical treatment. A specific injury caused your tear and it affects your shoulder stability. Your SLAP tear stems from overusing your shoulder. You have a SLAP tear because you regularly play sports in where you throw, such as baseball. SLAP tear surgery is a procedure used to repair injured shoulder cartilage. It involves making small incisions around the shoulder joint and using specialized instruments to repair or reconstruct .In Type 3, some of the torn labrum tissue is caught in the shoulder joint. A type 4 SLAP tear extends from the labrum all the way into the bicep. SLAP tear treatment depends on the severity. Don’t ignore a SLAP tear or try to play despite it. Untreated SLAP tears can worsen and eventually make it difficult to use your upper arm.
Positive pressure Leak Tester convenience store
A SLAP Lesion is a tear of the superior glenoid labrum near to the origin of the long head of biceps. The Anterior Slide Test for SLAP Lesions is a test used in orthopedic examination of the shoulder when testing for lesions to the superior aspect of the glenoid labrum. What are the different types of shoulder labral tears? The two most common types of labral injuries are the SLAP tear and Bankart tear. Both types of tears are usually accompanied by aching pain and difficulty performing normal shoulder movements. SLAP tears. SLAP stands for "superior labrum from anterior to posterior."The common symptoms of a SLAP tear are similar to many other shoulder problems. They include: A sensation of locking, popping, catching, or grinding . like the labrum, better than an X-ray. Sometimes, a special type of MRI, called an MRI arthrogram, is needed to see the SLAP tear. This test is performed by injecting dye into your shoulder .
performed by flexing shoulder to 90°, flex elbow to 90°, and forcibly internally rotate driving the greater tuberosity farther under the CA ligament. . most specific test for full thickness rotator cuff tear (specificity 98%) Infraspinatus. Infraspinatus Strength. . positive for SLAP tear when there is pain is "deep" in the glenohumeral .A SLAP tear can be hard to identify, because there are so many other things that can cause shoulder pain and because SLAP tears are not common. Ways to diagnose a SLAP tear include: A series of tests in which your doctor moves your shoulder joint around to see which movements are causing your pain. MRI.There are several types of labral tears: A SLAP lesion (superior labrum, anterior [front] to posterior [back]) is a tear of the labrum that usually occurs on the upper part of the socket and may also involve the origin, or starting point, of the long head of the biceps tendon.; A tear of the front part of the labrum at the bottom of the socket is called a Bankart lesion.
One point Heat-seal Tester convenience store
Basic usage. When it comes to your digital marketing strateg.
slap tear shoulder tests|special test for slap tear